All Generation Of Microprocessor
Fair child semiconductors (founded in 1957) invented the first Integrated Circuit in 1959 that marked the history. In 1968, Gordan Moore, Robert Noyce and Andrew Grove resigned from the Fair child semiconductors and started their own company: Integrated Electronics (Intel). In 1971, the first microprocessor Intel 4004 was invented. A microprocessor is also known as a central processing unit in which numbers of peripherals’ are fabricated on a single chip. It has ALU (arithmetic and logic unit), a control unit, registers, bus systems and a clock to perform computational tasks. Microprocessor History Architecture of MicroprocessorMicroprocessor is a single IC package in which a number of useful functions are integrated and fabricated on a single silicon semiconductor chip.
Its architecture consists of a central processing unit, a system bus and an input/output unit. Architecture of MicroprocessorThe system bus connects the various units to facilitate exchange of information. It further consists of data, address and control buses to perform data exchanging in a proper manner.The Central processing unit consists of one or more arithmetic logic unit (ALU), registers, and control unit.
Based on the registers also the generations of microprocessor can be classified. A microprocessor consists of general purpose and special type of registers to execute instructions and to store the address or data while running the program. The ALU computes all arithmetic as well as on data and specifies the size of microprocessor like 16 bit or 32 bit.The Memory unit holds the program as well as data and is divided into a processor, primary and secondary memory. The Input and output unit interfaces the I/O peripheral devices to microprocessor for accepting and sending information. 7 nguyen tc hp tac xa. Generation of Microprocessor1st Generation: This was the period during 1971 to 1973 of microprocessor’s history.
In 1971, INTEL created the first microprocessor 4004 that would run at a clock speed of 108 KHz. During this period, the other microprocessors in the market including Rockwell international PPS-4, INTEL-8008 and National semiconductors IMP-16 were in use. But, all these were not TTL compatible processors.2 nd Generation: This was the period during 1973 to 1978 in which very efficient 8-bit microprocessors were implemented like Motorola 6800 and 6801, INTEL-8085 and Zilogs-Z80, which were among the most popular ones. Owing to their superfast speed, they were costly as they were based on NMOS technology.3rd Generation: During this period 16 bit processors were created and designed using HMOS technology. From 1979 to 1980, INTEL 8086/6 and Motorola 68000 and 68010 were developed. Speeds of those processors were four times better than the 2nd generation processors.4th Generation: From 1981 to 1995 this generation developed 32 bit microprocessors by using HCMOS fabrication.
INTEL-80386 and Motorola’s 0 were the popular processors.5th Generation: From 1995 to until now this generation has been bringing out high-performance and high-speed processors that make use of 64-bit processors. Such processors include Pentium, Celeron, Dual and Quad core processors.Thus, microprocessor has evolved through all these generations, and the fifth generation microprocessors represent advancement in specifications. Therefore, some of the processors from the fifth generation of processors with their specifications are briefly explained below. Intel CeleronIntel Celeron is introduced in April 1998. It refers to a range of Intel’s X86 CPUs for value s. It is based on Pentium 2 and can run on all IA-32 computer programs. Jan4, 2004: Intel Celeron M processor 320 and 310 (1.3, 1.2 GHz).
July 20, 2004: Intel Celeron M processor Ultra Low voltage 353 (900 MHz). March- Intel Celeron M processor 430-450 (1.73-2.0 GHz). Nov 23: Intel Celeron D Processor 345 (3.06 GHz)The year 2008 marked the introduction of the following processor:. Jan 2008 Celeron Core 2 DUO (Allendale)PentiumPentium was introduced on March 2, in 1993. Pentium succeeded the Intel 486; The 4 indicates the fourth generation micro architecture in the microprocessor’s history. Pentium refers to an Intel’s single core x 86 microprocessor, which is based on the fifth generation micro-architecture. This processor’s name was derived from the Greek word penta, means five.The original Pentium processor was succeeded by the Pentium MMX in 1996.
History Of Microprocessor
This processor has a data bus of 64 bits. A standard single transfer cycle can read or write up to 64 bits at a time. The Burst read and writes back cycles are supported by the Pentium processors. These cycles are used for cache operations and transfer 32 bytes (size of the Pentium cache line) in 4 clocks. All cache operations are burst cycles for the Pentium.
Officially, Intel does not comment on unreleased products, which often has the knock-on effect that processors aren’t actually known about until the day they appear on shelves. In order to find information early (in order to prepare for launches), it comes down to software and retailers to expose the details, either accidentally or on purpose. From a couple of sources today, we now have a full list of Intel’s 8 th Generation processor stack, which is expected to launch during the first half of 2018, as well as some elements of Intel’s next 9 th generation products.We have already had six processors from Intel’s desktop 8 th Generation launch, called Coffee Lake, and a quartet of 8 th generation notebook Kaby Lake refresh processors also launched. These are both called 8 th generation, which can be confusing. Historically, Intel has never mixed and matched multiple microarchitecture designs in the same generation, but this changed when Murthy Renduchintala, Intel’s VP and GM of Client Computing and IoT, stated that ‘process tech use will be fluid based on segment’, indicating that within the same generation, there will be multiple microarchitectures at play.
History Of Intel Microprocessors

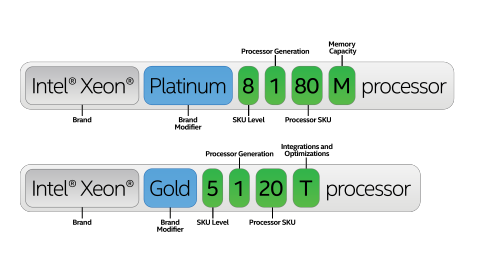
But along with the ten 8th Generation processors already launched, we have been expecting a broader stack of desktop and mobile parts, along with enterprise CPUs with ECC support.One of the things to also come out of these leaks is confirmation of Intel’s new product stack alignment:. Core i9. Core i7. Core i5. Core i3. (Core).
(Atom). Celeron G (Core). Celeron N/J (Atom)Pentium is now officially split between Gold and Silver, with Gold processors for the parts that use the Core microarchitecture, while Pentium Silver will be for Atom parts.

Intel’s 8 th Generation ProcessorsThe lists we have acquired starts with mobile processors. The key headline here is that Intel will be introducing the Core i9 brand to the mobile space, with one overclockable processor for now. Intel 8th Generation Mobile ProcessorsCoffee Lake-HSpecificationsare not confirmedCoresBaseFreqTurboFreqL3NominalTDP (PL1)Core i9-8950HK6 / 12??12 MB45 WCore i7-8850H6 / 12??12 MB45 WCore i7-8750H6 / 12??12 MB45 WCore i5-8400H6 / 6??9 MB45 WCore i3-8300H4 / 4??8 MB45 WWhat our sources do confirm is that all the i7-H and i7-HK processors will be based on Coffee Lake-H hardware, rather than Kaby Lake Refresh. This might be due to the 45W nature of the processors, and it is expected that the i3/i5/i7 naming will follow desktop Coffee Lake core counts, namely that Core i3 will be quad-core, Core i5 will be six-core and Core i7 parts will be six-core with hyperthreading. A Core i9 part in this context is undefined, but I expect it just to be an additional qualifier for a Core i7 mobile processor that is overclockable (hence it’s called an HK).This also means that the first Core i9 Coffee Lake processor is a mobile processor.Next up is the desktop list for 8th Generation Coffee Lake-S based processors. Six of these processors have already been launched (indicated with a.), so we can fill in a number of the gaps.
All Generation Of Microprocessor Computer
Sunday, November 26, 2017 - They are not corrupt. Intel has no idea what to do - it's far too big, it's lacking consistent vision, and perhaps the most important Intel's problem, is that its current top management haven't ever faced any big challenges - so they all think they are doing great. They are removed from reality, because middle management is blocking possibly critical problems from showing up on reports going up the chain, and they think any problem can be solved by combination of hard work and throwing money at the problem, but not exactly thinking. And last, but not least, they spent last 15 years collecting ambitious and brave directors, managers and engineers. And they are now occupied with chest-thumping, instead of doing something productive.Source: my brother works there.So, in the end, AMD got it's crap together, and here we have the effect. Monday, November 27, 2017 - Not to defend Intel too much, but meh, it was not considered illegal at the time, and it resulted in a settlement in civil court, not criminal convictions so not they were not convicted of the things you mention even if it seems to us that perhaps they should have been.It is basically impossible for a company with as many divisions and moving parts to avoid ever making a mistake. Also, activity that would be seen as legal at one stage, such as Intel doing co-branding bonuses with OEM's, can seem predatory at another, such as when they had a valid competitor and their marketshare had crossed 90%.
The rules change, and its not always obvious when it happens.